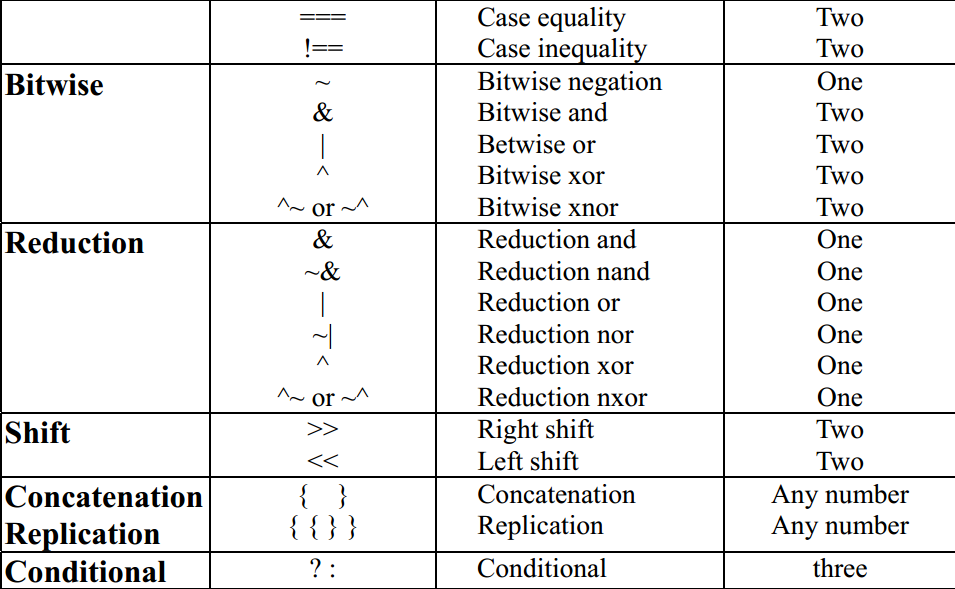
Reduction Operators
| Operator | Description |
| & | and |
| ~& | nand |
| | | or |
| ~| | nor |
| ^ | xor |
| ^~ or ~^ | xnor |
- Reduction operators are unary.
- They perform a bit-wise operation on a single operand to produce a single bit result.
- Reduction unary NAND and NOR operators operate as AND and OR respectively, but with their outputs negated.
- Unknown bits are treated as described before.
Example1 module reduction_operators();
2
3 initial begin
4 // Bit Wise AND reduction
5 $display (" & 4'b1001 = %b", (& 4'b1001));
6 $display (" & 4'bx111 = %b", (& 4'bx111));
7 $display (" & 4'bz111 = %b", (& 4'bz111));
8 // Bit Wise NAND reduction
9 $display (" ~& 4'b1001 = %b", (~& 4'b1001));
10 $display (" ~& 4'bx001 = %b", (~& 4'bx001));
11 $display (" ~& 4'bz001 = %b", (~& 4'bz001));
12 // Bit Wise OR reduction
13 $display (" | 4'b1001 = %b", (| 4'b1001));
14 $display (" | 4'bx000 = %b", (| 4'bx000));
15 $display (" | 4'bz000 = %b", (| 4'bz000));
16 // Bit Wise NOR reduction
17 $display (" ~| 4'b1001 = %b", (~| 4'b1001));
18 $display (" ~| 4'bx001 = %b", (~| 4'bx001));
19 $display (" ~| 4'bz001 = %b", (~| 4'bz001));
20 // Bit Wise XOR reduction
21 $display (" ^ 4'b1001 = %b", (^ 4'b1001));
22 $display (" ^ 4'bx001 = %b", (^ 4'bx001));
23 $display (" ^ 4'bz001 = %b", (^ 4'bz001));
24 // Bit Wise XNOR
25 $display (" ~^ 4'b1001 = %b", (~^ 4'b1001));
26 $display (" ~^ 4'bx001 = %b", (~^ 4'bx001));
27 $display (" ~^ 4'bz001 = %b", (~^ 4'bz001));
28 #10 $finish;
29 end
30
31 endmodule
& 4'b1001 = 0
& 4'bx111 = x
& 4'bz111 = x
~& 4'b1001 = 1
~& 4'bx001 = 1
~& 4'bz001 = 1
| 4'b1001 = 1
| 4'bx000 = x
| 4'bz000 = x
~| 4'b1001 = 0
~| 4'bx001 = 0
~| 4'bz001 = 0
^ 4'b1001 = 0
^ 4'bx001 = x
^ 4'bz001 = x
~^ 4'b1001 = 1
~^ 4'bx001 = x
~^ 4'bz001 = x
Shift Operators
| Operator | Description |
| << | left shift |
| >> | right shift |
- The left operand is shifted by the number of bit positions given by the right operand.
- The vacated bit positions are filled with zeroes.
Example
1 module shift_operators();
2
3 initial begin
4 // Left Shift
5 $display (" 4'b1001 << 1 = %b", (4'b1001 << 1));
6 $display (" 4'b10x1 << 1 = %b", (4'b10x1 << 1));
7 $display (" 4'b10z1 << 1 = %b", (4'b10z1 << 1));
8 // Right Shift
9 $display (" 4'b1001 >> 1 = %b", (4'b1001 >> 1));
10 $display (" 4'b10x1 >> 1 = %b", (4'b10x1 >> 1));
11 $display (" 4'b10z1 >> 1 = %b", (4'b10z1 >> 1));
12 #10 $finish;
13 end
14
15 endmodule
4'b1001 << 1 = 0010
4'b10x1 << 1 = 0x10
4'b10z1 << 1 = 0z10
4'b1001 >> 1 = 0100
4'b10x1 >> 1 = 010x
4'b10z1 >> 1 = 010z
Concatenation Operator
- Concatenations are expressed using the brace characters { and }, with commas separating the expressions within.
- Example: + {a, b[3:0], c, 4'b1001} // if a and c are 8-bit numbers, the results has 24 bits
- Unsized constant numbers are not allowed in concatenations.
Example1 module concatenation_operator();
2
3 initial begin
4 // concatenation
5 $display (" {4'b1001,4'b10x1} = %b", {4'b1001,4'b10x1});
6 #10 $finish;
7 end
8
9 endmodule
{4'b1001,4'b10x1} = 100110x1
Replication Operator
Replication operator is used to replicate a group of bits n times. Say you have a 4 bit variable and you want to replicate it 4 times to get a 16 bit variable: then we can use the replication operator.
| Operator | Description |
| {n{m}} | Replicate value m, n times |
- Repetition multipliers (must be constants) can be used:
- {3{a}} // this is equivalent to {a, a, a}
- Nested concatenations and replication operator are possible:
- {b, {3{c, d}}} // this is equivalent to {b, c, d, c, d, c, d}
Example1 module replication_operator();
2
3 initial begin
4 // replication
5 $display (" {4{4'b1001}} = %b", {4{4'b1001}});
6 // replication and concatenation
7 $display (" {4{4'b1001,1'bz}} = %b", {4{4'b1001,1'bz}});
8 #10 $finish;
9 end
10
11 endmodule
{4{4'b1001} = 1001100110011001
{4{4'b1001,1'bz} = 1001z1001z1001z1001z
Conditional Operators
- The conditional operator has the following C-like format:
- cond_expr ? true_expr : false_expr
- The true_expr or the false_expr is evaluated and used as a result depending on what cond_expr evaluates to (true or false).
Example
|
| 1 module conditional_operator(); 2 3 wire out; 4 reg enable,data; 5 // Tri state buffer 6 assign out = (enable) ? data : 1'bz; 7 8 initial begin 9 $display ("time\t enable data out"); 10 $monitor ("%g\t %b %b %b",$time,enable,data,out); 11 enable = 0; 12 data = 0; 13 #1 data = 1; 14 #1 data = 0; 15 #1 enable = 1; 16 #1 data = 1; 17 #1 data = 0; 18 #1 enable = 0; 19 #10 $finish; 20 end 21 22 endmodule |
time enable data out
0 0 0 z
1 0 1 z
2 0 0 z
3 1 0 0
4 1 1 1
5 1 0 0
6 0 0 z
Operator Precedence
| Operator | Symbols |
| Unary, Multiply, Divide, Modulus | !, ~, *, /, % |
| Add, Subtract, Shift | +, - , |
| Relation, Equality | ,=,==,!=,===,!== |
| Reduction | &, !&,^,^~,|,~| |
| Logic | &&, || |
| Conditional | ? : |
Bạn Có Đam Mê Với Vi Mạch hay Nhúng - Bạn Muốn Trau Dồi Thêm Kĩ Năng
Mong Muốn Có Thêm Cơ Hội Trong Công Việc
Và Trở Thành Một Người Có Giá Trị Hơn